
Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions worldwide. Proper management of diabetes is essential to lead a healthy and fulfilling life. In this article, we'll provide you with 10 crucial tips for maintaining diabetes and highlight the top 10 common symptoms to watch out for. We'll also discuss important pathology tests and potential related disorders or diseases.
Decoding Diabetes
In the realm of medical terms, "disease" and "disorder" hold nuances worth exploring, especially in the context of diabetes.

Disease
A disruption in the body's norm, often instigated by pathogens, genetics, or environment.
Disorder
A broader term, encompassing structural or functional abnormalities arising from genetics, development, or lifestyle.

Diabetes, tagged a metabolic disorder, exemplifies this contrast. It hinders blood sugar regulation—Type 1 through inadequate insulin, Type 2 through resistance. Complex interplays between genes and lifestyle are at play, defying a single infectious cause.
While "disorder" is more commonly used, the terms can intertwine. What matters is understanding the condition to manage it effectively.
Why Does It Occurs?
Diabetes occurs due to a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors that disrupt the body's ability to regulate blood sugar (glucose) effectively. There are primarily two main types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2, each with its own underlying causes.
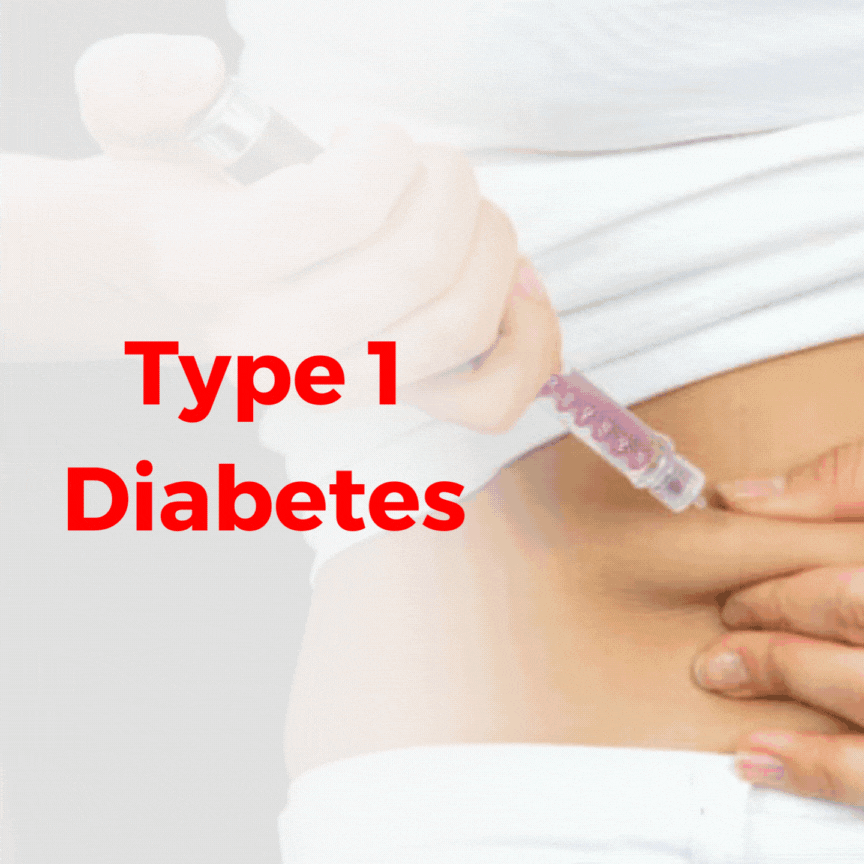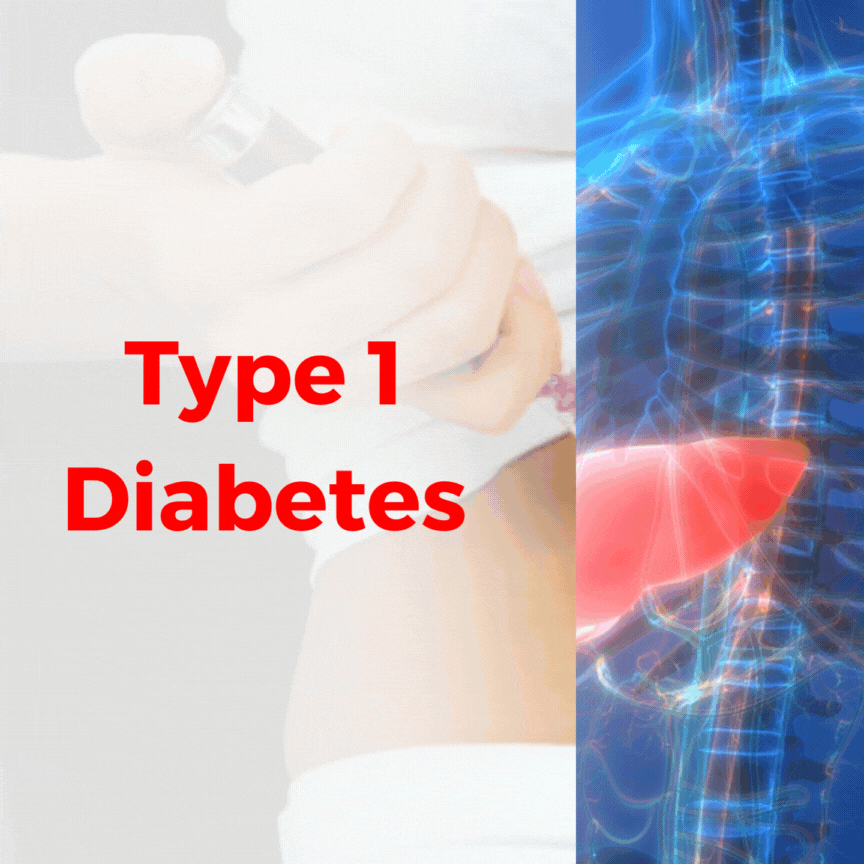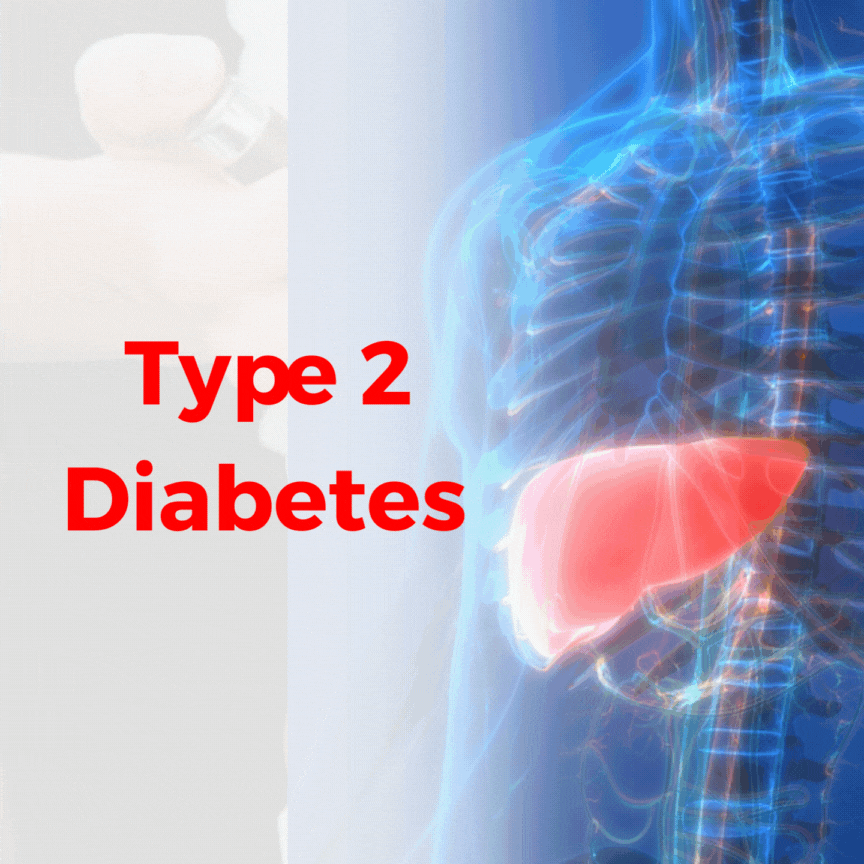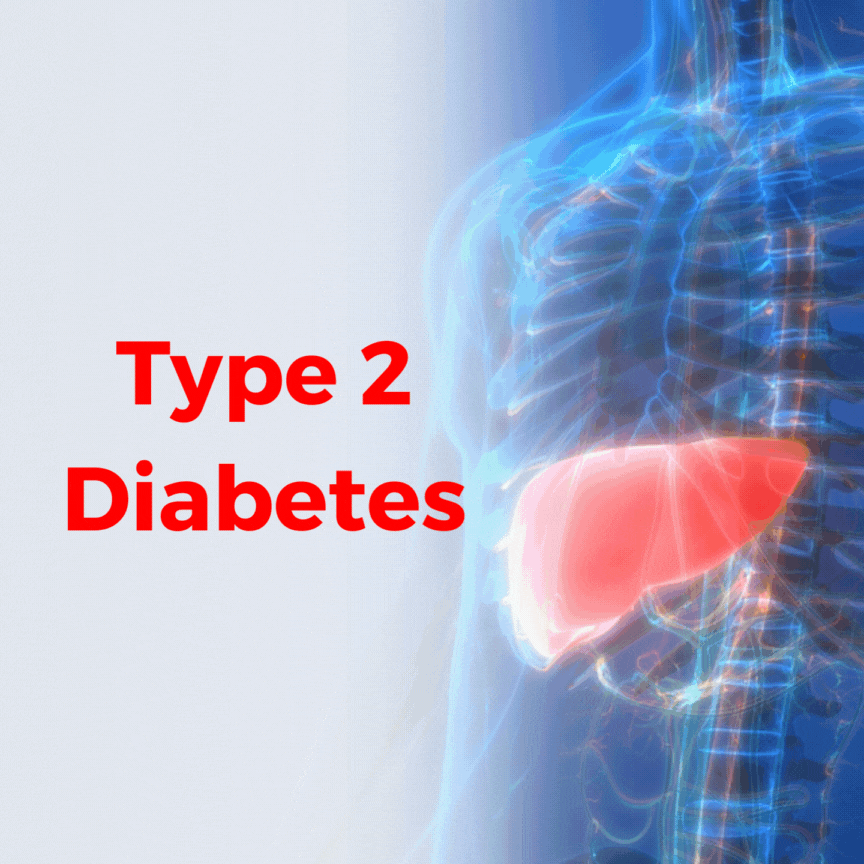
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells (beta cells) in the pancreas. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy. Without sufficient insulin, blood sugar levels rise, leading to various health issues.
The exact cause of Type 1 diabetes isn't fully understood, but it's believed to involve a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers, such as viral infections. It often develops early in life and is not preventable.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is primarily driven by a combination of insulin resistance and inadequate insulin production. Insulin resistance occurs when cells become less responsive to insulin's effects, causing the body to need more insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. Over time, the pancreas may struggle to produce enough insulin to meet the body's needs.
The main risk factors for Type 2 diabetes include:
Genetics: Family history of diabetes can increase the risk.
Lifestyle: Poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity contribute significantly.
Age: The risk increases with age, particularly after 45.
Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups have a higher risk.
High Blood Pressure: Hypertension is a risk factor for Type 2 diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes: Women who had gestational diabetes during pregnancy are at higher risk.
Other Types
There are also other types of diabetes, such as gestational diabetes that occurs during pregnancy and secondary diabetes caused by other medical conditions or medications. In summary, diabetes occurs when the body's mechanisms for regulating blood sugar are disrupted. The exact reasons can vary based on the type of diabetes. Genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices, environmental factors, and immune system dysfunction all play roles in the development of diabetes. Early detection, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate medical care are crucial for managing diabetes effectively.

10 Tips for Managing Diabetes:
Balanced Diet: Focus on a well-balanced diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Monitor carbohydrate intake and consider consulting a dietitian for personalized guidance.
Regular Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise to help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Medication Adherence: If prescribed medication, take it as directed by your healthcare provider. Consistent medication adherence is crucial for managing blood sugar levels.
Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels as recommended by your healthcare provider. This helps you make informed decisions about your diet, exercise, and medication.
Stress Management: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga. Stress can affect blood sugar levels, so managing it is essential.
Adequate Sleep: Prioritize getting enough quality sleep. Sleep deprivation can impact insulin sensitivity and overall diabetes management.
Hydration: Stay hydrated with water throughout the day. Avoid sugary drinks that can cause blood sugar spikes.
Foot Care: Inspect your feet daily for any cuts, sores, or blisters. Diabetes can affect circulation and sensation, making foot care important to prevent complications.
Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor your diabetes and address any concerns.
Education and Support: Learn about diabetes and connect with support groups or healthcare professionals who specialize in diabetes management. Education empowers you to make informed decisions.
Top 10 Common Symptoms of Diabetes:
Frequent Urination: Excessive urination, especially at night (nocturia).
Excessive Thirst: Feeling unusually thirsty and needing to drink more fluids.
Increased Hunger: Frequent hunger even after eating.
Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired, even with sufficient rest.
Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying, often accompanied by increased appetite.
Blurred Vision: Vision changes, including difficulty focusing.
Slow Healing: Cuts, bruises, or infections that take longer to heal.
Numbness or Tingling: Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet, a symptom of neuropathy.
Dry Skin: Skin dryness and itchiness, often due to poor circulation.
Recurrent Infections: Frequent infections, particularly yeast infections or urinary tract infections.

Pathology Tests and Related Disorders:
HbA1c Test: Measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
Fasting Blood Sugar Test: Measures blood sugar levels after fasting overnight.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: Evaluates how your body processes sugar after consuming a sugary drink.
Related Disorders or Diseases:
Diabetic Neuropathy: Nerve damage caused by high blood sugar levels.
Diabetic Retinopathy: Damage to the blood vessels in the retina due to diabetes.
Diabetic Nephropathy: Kidney damage resulting from long-term diabetes.
Cardiovascular Disease: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.

Conclusion: By following these 10 tips for diabetes management and staying vigilant for common symptoms, you can take control of your health and lead a fulfilling life with diabetes. Regular monitoring, lifestyle changes, and proper medical care are key to effectively managing this chronic condition. If you experience any symptoms or concerns, consult your healthcare provider promptly to ensure timely intervention and a better quality of life.